ENVIRONMENTAL RESPONSIBILITY
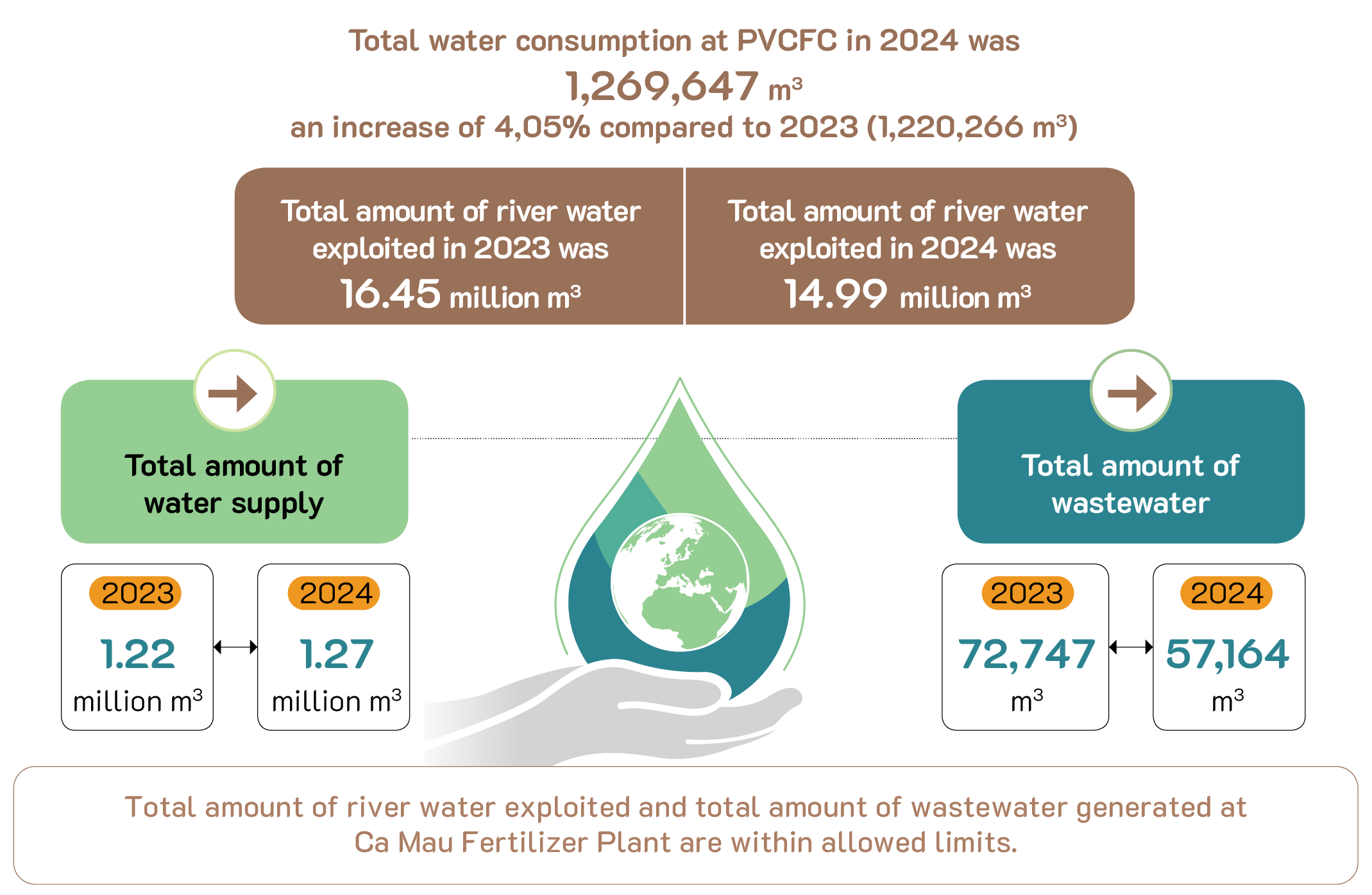
The Company always strictly complies with current legal regulations of the law and manages according to ISO 14001:2015 standards (presented in PVCFC Company’s quality, safety, environmental, inspection and testing policies) to conduct environmental control at work. All waste sources of the Plant are strictly controlled and minimized in quantity, quality control always meets allowed regulations before being discharged into the environment. In 2024, the Company recorded no case of environmental violation.
- Number of violations: 0
- Total amount of fines: 0
Since its establishment, PVCFC has always focused on building an environmental management and control system. The Company strictly complies with regulations on safety, firefighting and prevention and environment such as: building an online monitoring system to continuously monitor and track the plant’s emission activities and transmit data to the Department of Natural Resources and Environment for management and supervision; quarterly environmental monitoring results are publicly posted on the Company’s website in the QHSE section. Management methods and environmental performance index for each specific content are described as below.